The following table includes some conditional operators that help in the control flow of the Dart program:
| Operator | Description |
| = = | Equal to |
| = ! | Not Equal to |
| < | Less than |
| = < | Less than or equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| = > | Greater than or equal to |
| ? | Return value of two expressions |
| ?? | Return the which is not equal null value of two expressions |
| is | Is |
| !Is | Is Not |
Example: In the following code, you will test the role of double equal sign "= =" whichis used to compare if two values are equal or not. If they are equal, then the run result will be true; otherwise, the run result will be false.
main() {
int x=3;
int y=5;
print(x==y);
}
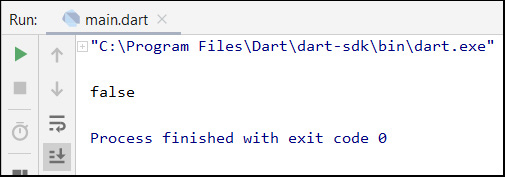
The run result of this code follows:
Example:
The following Dart conditional operator "?" will return one expression (exp1 or exp2) as illustrated in the following figure :

The following code has an example about using "?" Dart conditional operator:
main() {
var Age=20;
var x=Age >18 ? "Allow" : "Deny";
print(x);
}
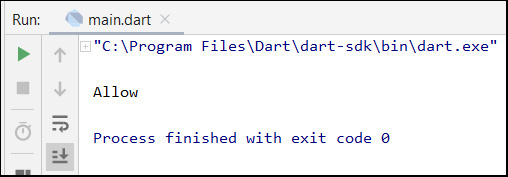
Because the "Age" value in this example is 20, the condition result is true, so the run result will be Allow as illustrated in the following figure:
Example:
In the following example, the conditional operator "??" is used to compare two expressions, and then return the value of the expression which is not equal to a null value as illustrated in the following code:
main() {
var x=null;
var y=10;
var z=x ?? y ;
print(z);
}
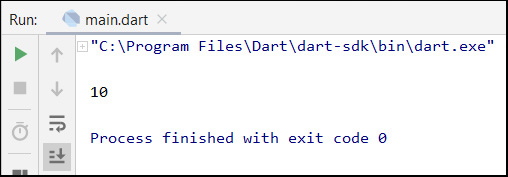
The run result of this code follows:
Example:
The following code displays using "is" operator. If the condition operator result is true, the output will be true; otherwise, the result will be false.
main() {
int x=5;
print(x is bool);
}
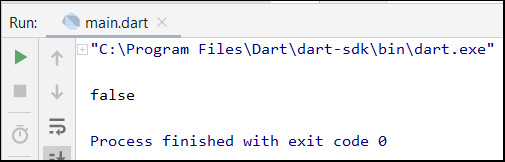
The run result of this code follows:
* This topic is a part of lesson 2 of Flutter Application Development course. For more information about this course, click here.
