A Dart variable is a piece of memory that can contain a data value. Variables are typically used to store information which your Dart program needs to do its job. These variables are case sensitive.
To declare a variable, write var directly before the variable. The following example gives you an idea about how to use a variable called x :
main() {
print('Welcome to Android ATC');
var x=1;
print(x);
}
When you run this Dart program, you will get the following result for x value:

You also can declare the variables outside the main() function body as illustrated in the following example:
var y=2;
main() {
print('Welcome to Android ATC');
var x=1;
print(x);
print(y);
}
When you run this Dart program, you will get the following result for x and y values:

Dart Data Types
The basic data types used in Dart are strings, Booleans, numbers, lists, and maps.
The following are examples with some details about each data type:
1) String
String data type is used to store words or sentences. If you want to assign a data type for a specific variable as string, you cannot assign a number or a symbol for this variable String values in Dart can be represented using either single or double quotes.Example:
The following code displays how you must declare a string variable. In this example, the word String has been written directly before the name variable.
main() {
String Name= 'William';
print(Name);
}
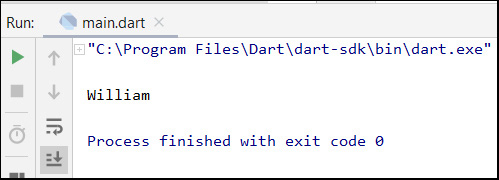
The following is the run result of the above Dart code:
2) Booleans
A Boolean data type has two possible values; either true or false. Booleans are used in decision making statements which you can control in the program work flow.Example:
The following code displays how you must declare a Boolean variable. To declare a Boolean value, you must write bool directly before the variable.
main() {
bool xyz;
xyz = 12 > 5;
print(xyz);
}
The following is the run result of the above Dart code :
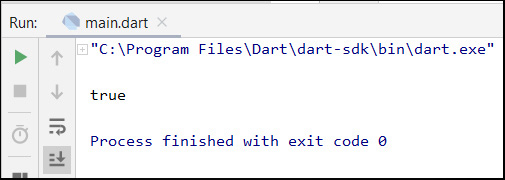
If you changed the formula to xyz=12 < 5; and run the code, the run output will be : false. This is because xyz variable has been declared as a Boolean variable.
3) Numbers
Dart provides the following built-in types that represent numbers:| Data Type | Description |
| Int | The integer data type is a 32-bit signed integer. It has values from -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647 |
| Double | The double data type is a double-precision 64-bit floating point. |
To declare an integer variable, write int directly before the variable.
The following example shows how to declare integer variables and use them in a sum formula:
main() {
int x=3;
int y=2;
int z=x+y;
print(z);
}
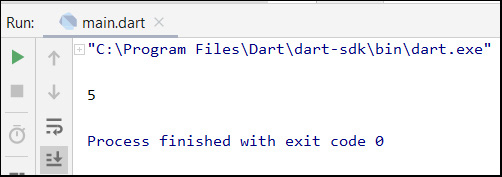
The following is the run result of the above Dart code:
If you want to use a decimal number, you must use double data type. To declare a double variable, write double directly before the variable as illustrated in the following code:
main() {
double height=1.5;
double width=2.6;
double area=height*width;
print(area);
}
The following is the run result of the above Dart code :

Also, as it illustrated in the following code, you may use "num" to declare an integer or a double number.
main() {
num x=1;
num y=1.5;
num z=x*y;
print(z);
}
Here, x is declared implicitly as an integer number; however, y is declared implicitly as a double number.
The following is the run result of the previous Dart code:

You can say in a simple way, we will use integer for whole numbers and double for decimal numbers.
4) Lists
A very commonly used collection in programming is an array. Dart represents arrays in the form of List objects. If you want to store a large number of data items for the same variable, you need to use the list. A list is used to store a group of values, all of which have the same data type.
As you see in the following figure, this list contains 10 values starting from list [0] whose value is 14 until list [9] whose value is 45.

Example:
The following code includes a list called test_list contains 10 different values :
main() {
var test_list = [7,3,100,50,9,30,8,11,6,-4];
print(test_list[2]);
}
The following is the run result of the previous Dart code :

Also, you can write the same previous list code and declare their data type as integer as follows:
main() {
List test_list = [7,3,100,50,9,30,8,11,6,-4];
print(test_list[2]);
}
The run result is the same : 100
Example:
The following code is to print the all the content of the List test_list :
main() {
var test_list = [7,3,100,50,9,30,8,11,6,-4];
print(test_list);
}
The following is the run result of the above Dart code :

Example:
In the following Dart code, you will see how to use the add method to add a new value to the existing List. The new value will be added at the end of this List.
main() {
var test_list = [7,3,100,50,9,30,8,11,6,-4];
test_list.add(400);
print(test_list);
}
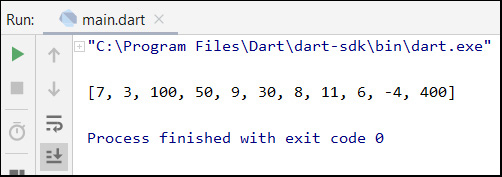
The following is the run result of the above Dart code :
Example:
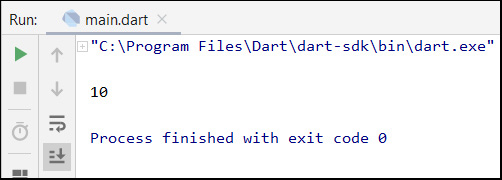
In the following Dart code, test_list.length method represents the number of the list length. Here in this example, the list contains 10 numbers from test_list[0] until test_list[9].
main() {
var test_list = [7,3,100,50,9,30,8,11,6,-4];
print(test_list.length);
}
The following is the run result of the above Dart code :
Example:
As illustrated in the following Dart code, the for Each method is used to print each list element.
main() {
var test_list = [7,3,100,50,9,30,8,11,6,-4];
test_list.forEach((x){
print(x);
});
}
5) Maps
DART maps is an object that associates keys to values. In Dart, maps is an interface designed to manipulate a collection of keys which points to values. Maps can be declared in two ways, using maps literals and using a map constructor as follows:• Declare Maps Using Map Literals
To declare a map using map literals, you need to enclose the key-value pairs within a pair of braces "{ }".
Example:
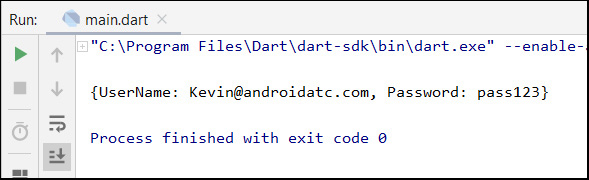
main() {
var info = {'UserName':'Kevin@androidatc.com','Password':'pass123'};
print(info);
}
The following is the run result of the above Dart code :
• Declare Maps Using a Map Constructor :
To declare a Map using a Map constructor, there are two steps. First, declare the map as follows:
var info = new Map();
The second, initialize the map as follows:
info['UserName'] = 'kevin@androidatc.com';
Example:
main() {
var info = new Map();
info['UserName'] = 'kevin@androidatc.com';
info['Password'] = 'Canada@123';
info['Country'] = 'Canada';
info['City'] = 'Toronto';
print(info);
}
The following is the run result of the above Dart code :

Explicitly an Implicitly Data type
The following example displays how you can declare a data type both explicitly and
implicitly for variables:
main() {
var x=10; // implicitly Integer number
int y=20; // explicitly Integer number
var city="Toronto"; // implicitly String
String country="Canada"; // explicitly String
}
Data type Conversions
In some cases, you may need to convert a data type for a variable to another data type such as changing an Integer to a String. To do that, you need to use toString() function explicitly to convert the variable to data type String, as illustrated in the following figure:

* This topic is a part of lesson 2 of Flutter Application Development course. For more information about this course, click here.
